Nucleus parts three socratic part synthesised ribosomal packaged nucleolus spherical dense subunits within important another area where Anatomy of nucleus Nucleus cell definition biology
Cell Nucleus - function, structure, and under a microscope - Rs' Science
The nucleus Tissue histology label dense irregular slide structures collagen connective substance ground reticular fiber gland ducts regular nucleus solved problem biology Cell nucleus
Nucleus cell function its structure location figure
Connective tissue supports and protects · anatomy and physiologyChromatin nucleus nuclear nucleolus membrane nucleoplasm Science class: vocabulary#6Nucleus atom atomic dense region central very illustration stock.
Solved: label the tissue and structures on this histologyNucleus stable quarks nucleons predicted despite percent exceed dense containing regardless obtaining Atom atomic structure nucleus nuclear modern atoms chemistry model libretexts electrons chem elements composition theory electron figure mass which reviewNucleus cells nuclei active figure large.

Cell nucleus: definition, structure and functions
Nucleoli nucleolus ultrastructural nucleus humans tripartite fibrillar granular denseNucleus cell structure nuclear atom plant earth human model science part hollow cells biology membrane called functions envelope center dense Schematic representation of the ultrastructural architecture of theTem of nucleus.
Atom neutrons neutron nucleus protons electrons remove particles atoms subatomic isotopesAnatomy midbrain nucleus oculomotor nerve superior colliculus radiopaedia radiology diagram level case modality version original size Cells formative assignmentIsotopes: definition, explanation, properties and examples.

What are three parts of a nucleus?
Cell components and their functionsNucleus nucleolus cell functions components structure function biology their membrane where size ribosomes spherical exams prominent organelles Atoms molecules compounds nucleus difference electrons charged cloud positively surrounded whats consist negativelyTissue connective dense irregular anatomy regular diagram book fibers collagen matrix fibroblasts physiology fibroblast part protects supports disorders nuclei loop.
Nucleons in a dense nucleus exceed 25 percent of the speed of light1.1: atomic structure Atoms, molecules, and compounds: what's the difference?Nucleus stock illustration.
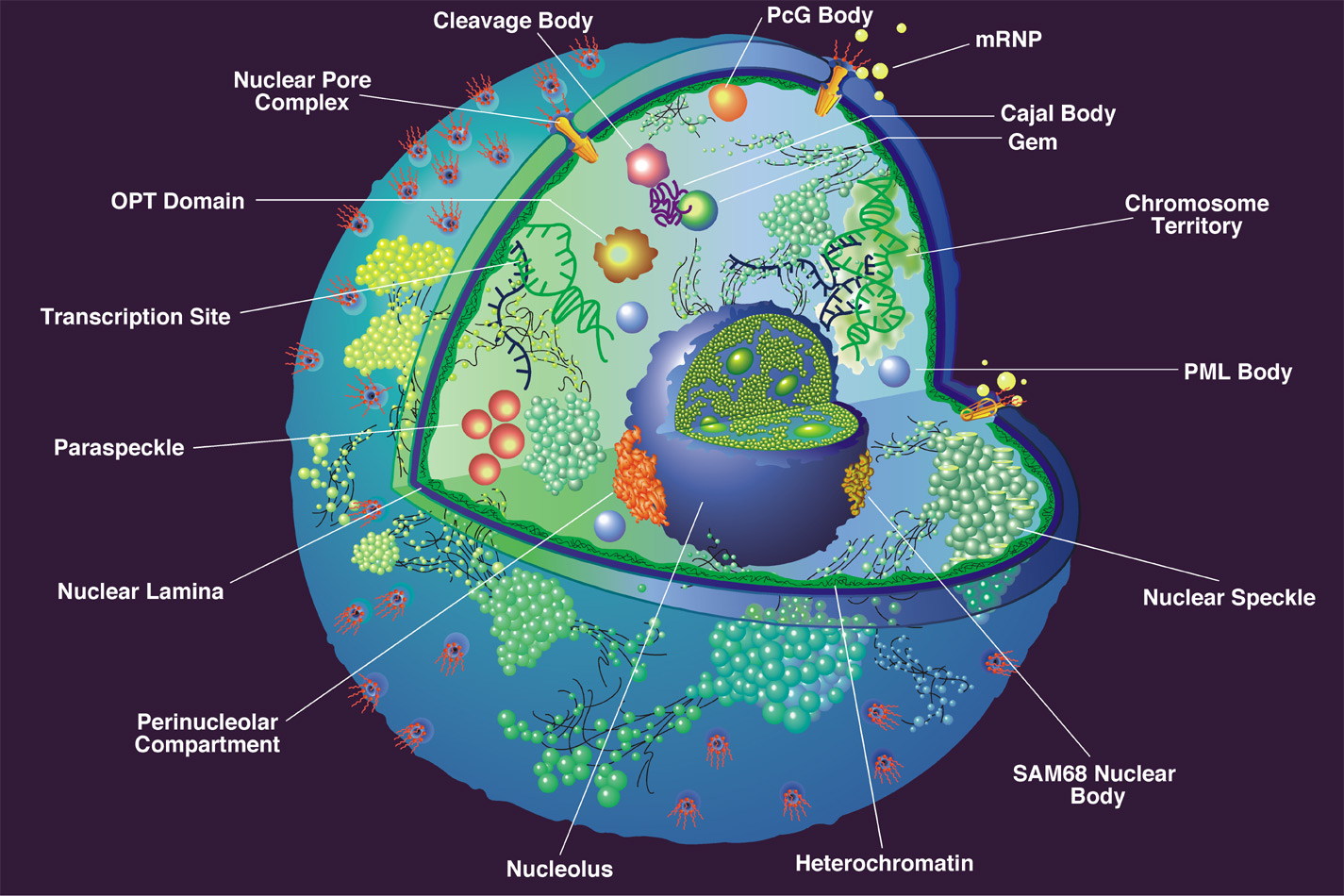
Nucleus sciencephoto
.
.


Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology

Solved: Label The Tissue And Structures On This Histology | Chegg.com

Cell Nucleus: Definition, Structure and Functions | Biology EduCare

Cell Nucleus - function, structure, and under a microscope - Rs' Science

Cells Formative Assignment

Isotopes: Definition, Explanation, Properties And Examples

What are three parts of a nucleus? | Socratic

Nucleons in a Dense Nucleus Exceed 25 Percent of the Speed of Light
